Anyone can get DVT at any time but there are risk factors that can increase your chances of developing this condition. Even if varicose veins represent the main cause of SVT several underlying conditions eg malignancy thrombophilia autoimmune diseases should be sought especially in idiopathic migrant or recurrent SVT of nonvaricose vein patients.
 Risk Factors For Venous Thromboembolism Download Table
Risk Factors For Venous Thromboembolism Download Table
21 46 Farmer RD Lawrenson RA Todd JC et al.
Thrombosis risk factors. Psychosocial risk factors such as low socioeconomic status depression and stress Inflammatory and autoimmune disease such as rheumatoid arthritis. Recent or recurrent cancer. Its also more commonly seen in people who.
A history of DVT. SVT and VTE share many common predisposing risk factors. Family history of VTE.
These deposits cause the arteries to harden and narrow over time and increase the risk of blood clots. Indeed common risk factors may be present which implies a noncausal association 46. For example women who are pregnant or taking birth control are at risk of developing blood clots.
Major risk factors for thrombosis other than age include exogenous factors such as surgery hospitalization immobility trauma pregnancy and the puerperium and hormone use and endogenous factors such as cancer obesity and inherited and acquired disorders of hypercoagulation. What are the symptoms of thrombosis. 12 Risk of cancer-associated thrombosis is multifactorial.
Risk Factors of Deep Vein Thrombosis. Additional risk factors such as previous VTE increasing age cardiac or respiratory failure prolonged immobility presence of central venous lines estrogens and a wide variety of inherited and acquired hematological conditions contribute to an increased risk for VTE. Medical illness for example acute infection.
A comparison of the risks of venous. Risk factors for arterial thrombosis may include. Lack of movement such as after surgery or on a long trip.
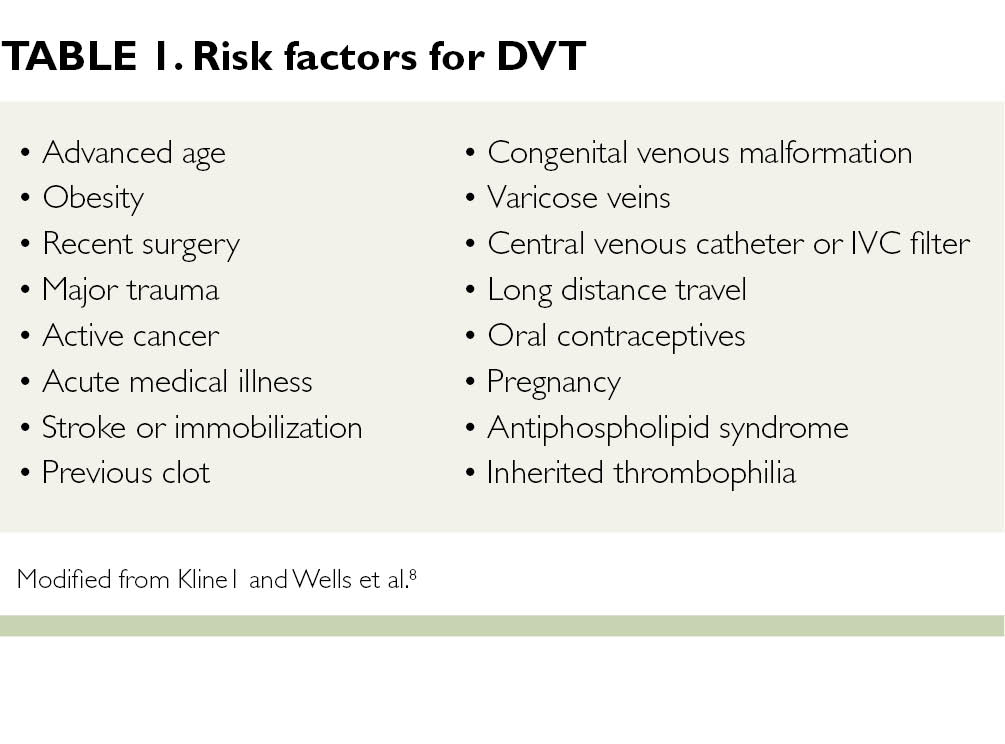
Risk factors for DVT. Acquired or familial thrombophilia. Cancer known or undiagnosed.
3 A number of risk factors have been reported and among them treatment-related factors such as chemotherapy eg platinum based antiangiogenesis agents and hormonal. Family history of arterial thrombosis. Estrogen-based medicine such as hormonal birth control or hormone replacement therapy.
Other factors include surgery head trauma arterio-venous malformations infection paraneoplastic and autoimmune disease. 1 If you live with a chronic condition like. Age over 60 years.
Trauma surgery and cancer. Deep vein thrombosis DVT is more likely to occur in people with continuing or intrinsic risk factors such as. Lack of activity and obesity.
Patients with cancer are at an increased risk of venous thromboembolism VTE and arterial thromboembolism ATE. Finally major risk factors for arterial thrombosis eg. Redness of the skin.
This is known as atherosclerosis. This article presents a comprehensive review of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis etiologies. Of the major risk factors for myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke such as obesity smoking diabetes hypertension and dyslipidemia only obesity has been consistently reported as a moderate risk factor for venous thrombosis 46.
Causes of arterial thrombosis Arterial thrombosis usually affects people whose arteries are clogged with fatty deposits. During and just after pregnancy. DVT occurs most commonly in people age 50 and over.
Know the Signs Symptoms and Risk Factors. Thromboembolic disease in association with different combined oral. Being overweight or obese.
Tobacco smoking blood pressure and cholesterol are contrasted with major risk factors for venous thrombosis eg. Each persons symptoms may vary. Are overweight or obese.
