Vaccines work by helping people safely imitate natural infections. Once the antigen-specific antibodies are produced they work with the rest of the immune system to destroy the pathogen and stop the disease.
Vaccines University Of Leicester
Many of them produce few to no antibodies in response to a vaccine or an infection leaving them susceptible to the virus.
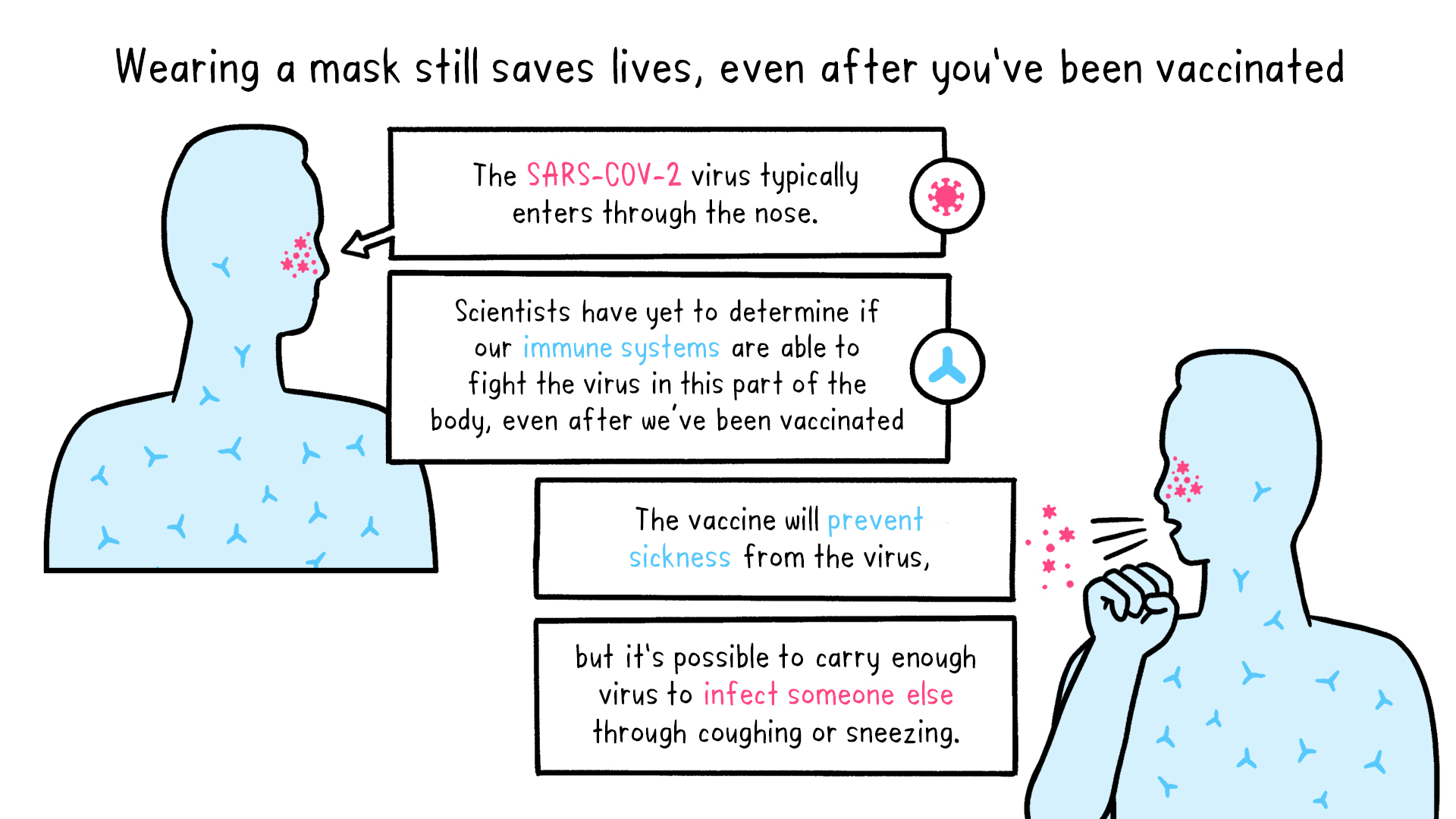
Do vaccines work after infection. Vaccines help develop immunity by imitating an infection. Vaccines once injected dont shield the body from infection. He used vaccines such as the chicken pox shingles and influenza as examples.
Instead they equip the immune system with a sophisticated alarm systemone that will trigger a vigorous and rapid response. Some of this is due to individual variation in our response to a given vaccine. The vaccine fails in 5 of cases.
To be clear its important to get vaccinated when your turn comes. In reality it is actually extremely difficult to produce vaccines that stop virus infection altogether. When they do become infected they may suffer prolonged illness with.
In an ideal world all vaccines would induce sterilising immunity. Even if a vaccine fails to protect against infection it often protects against serious disease he said. In the early stages if memory B cells detect any persistent infection or vaccine.
Some people may still get COVID-19 despite having a vaccination. Like all medicines no vaccine is completely effective so you should continue to take recommended precautions to avoid infection. Food and Drug Administration FDA might decide to consider whether one dose is enough for people whove had a prior COVID-19 infection.
But a vaccine that provides sterilising immunity stops the virus in its tracks. A vaccine mimics this primary infection providing antigens that prime the adaptive immune system and generating memory cells that can be activated rapidly in the event of a real. But were still learning how vaccines will affect the spread of COVID-19.
When a disease-causing agent such as virus or bacteria invades your body your immune system recognises it as harmful and will trigger a response to destroy it. After you are fully vaccinated against COVID-19 you may be able to start doing some things that you had stopped doing because of the pandemic. Vaccines do work during incubation period of virus or bacteria but not after the start of diseaseevery virus or bacteria has a incubation period if a virus or bacteria gets into the body of a person then it has to replicate there up to an extent to which it can become strong enough to cause an infection these period of replication is incubation period within this period vaccine works 100 but after incubation period.
As explained here by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC vaccines are used to prevent rather than treat infection. The immune system is a network of cells tissues and organs that work together to help fight off infection from harmful bacteria or viruses. VirusesBacteria and Your Immune System.
If other studies support these results the US. If you get vaccinated no doubt youre less likely to get the flu he explained. How does vaccination work.
Vaccines can be developed for bacterial or viral infections. After theyve had their COVID-19 active infection. Antibodies to one pathogen generally dont protect against another pathogen except when two pathogens are very similar to each other like cousins.
This type of infection however almost never causes illness but it does cause the immune system to produce T-lymphocytes and antibodies. The reason she explains is that those who developed the infection previously have an immune system that is already primed to fight it off. Most vaccines that are.
Sometimes after getting a vaccine the imitation infection can cause minor symptoms such as fever. The first sign that the strategy is working will be a fall in hospital admissions and deaths and if the vaccines prevent transmission as well as illness then a fall in new infections as the. There is simply no evidence to suggest that a vaccine produces a better immune response than infection.
The second study examined more than 7000 hospital staff and found about a 75 reduction in infections with Pfizers vaccine. Our bodys ability to maintain antibody levels following infection or vaccination is a result of two mechanisms. That means that vaccines help protect you from diseases without ever having to risk the serious and sometimes deadly consequences of getting sick from those diseases.
There have been studies done with pertussis that show infection does produce a substantially longer protection than a vaccine. Vaccines work with your immune system so your body will be ready to fight the virus if you are exposed. But these findings do suggest that a single dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines can produce a rapid and strong immune response in people whove already recovered from COVID-19.
There are many reasons why vaccination or infection do not always provide protection that is long lasting.