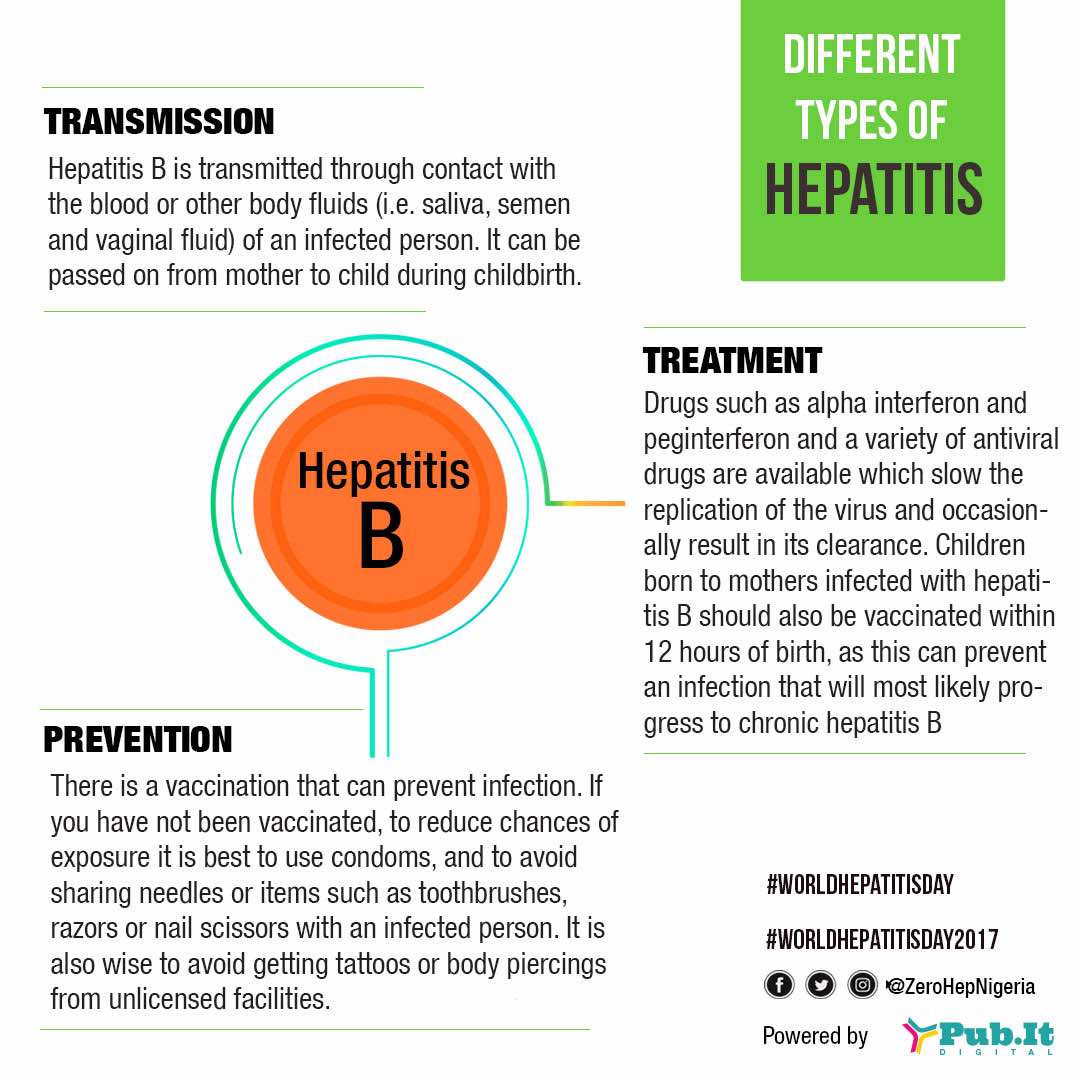
Results from several large case-control studies and cohort studies representing various populations suggest that family history is a major risk factor in prostate cancer. However it was not considered as a stronger factor than the serum prostate-specific antigen PSA level for the diagnosis of prostate cancer.
 Major Risk Factors For Prostate Cancer That You Can T Change
Major Risk Factors For Prostate Cancer That You Can T Change
People with a family history of breast ovarian or prostate cancer have an increased risk of breast cancer 28.

Family history of prostate cancer. Fifty-one thousand eight hundred ninety-seven brothers of 32 807 men with prostate cancer were identified in Prostate Cancer data Base Sweden PCBaSe. Family history and family or personal history of high-risk germline mutations are included in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network NCCN guidelines for the early detection of prostate cancer. In fact it might lead to men having treatment for prostate cancer even though that cancer wouldnt have caused any problems or symptoms.
If you have two or more close male relatives who have been diagnosed your lifetime risk of developing prostate cancer increases five-fold. Urology 67 10281032 2006. Having a father who developed prostate cancer at a younger age does not automatically mean that you too will develop prostate cancer.
Now researchers from Sweden have calculated just how much having a brother or father with prostate cancer or both raises the risk. 14 18 19 A family history of a brother or father with prostate cancer increases the risk of prostate cancer and the risk is inversely related to the age of the affected relative. It is well established that if a woman has a family history of.
Jennifer Beebe-Dimmer lead author of the study said that these new findings highlight the need for doctors to ask about all cancer diagnoses among family members even cancers found in the opposite sex. Your Family History The Facts If your father or brother have ever been diagnosed with prostate cancer you have twice the average risk of developing the disease. Family history of prostate cancer among sibling was associated with a 17 increased risk of ovarian cancer 95 CI 103 to 134 however no significant association was found between family history of prostate cancer among parent and risk of ovarian cancer RR 119 95 CI 084 to 170.
15 - 19 However at least some familial aggregation is due. The increased risk is likely due to genetic factors but may also be due to shared lifestyle factors or other family traits. Whether you are Caucasian or African-American or a citizen of the United States or Japan family history is a strong factor for prostate cancer predisposition.
Men with a family history of both cancers were also at elevated risk. We provide age-specific probabilities of non-low- and high-risk prostate cancer. Family history is a major risk factor for development of the disease.
Wayne State University researchers looked at the family histories of these women and determined the risks associated with both prostate and breast cancer. The history should include age at diagnosis of prostate cancer in both paternal and maternal lineages and a complete list of other cancers. Family history of prostate cancer alone was associated with a 68 increased risk of total disease 95 CI 153-183 and a 72 increased risk of lethal disease 95 CI 125-238.
A family history of prostate cancer may increase womens risk for breast cancer. Factors suggestive of a genetic contribution to prostate cancer include the following. How Family History Affects Prostate Cancer Risk September 8 2016 It has long been known that men with a family history of prostate cancer are at higher risk of getting it themselves.
Female family members with a history of breast cancer. If you have a family history of prostate cancer or breast ovarian pancreatic or colorectal cancer I would encourage you to discuss this information with your healthcare provider to see if genetic counseling and testing are appropriate so you can determine what your options are for cancer screening for you and other members of your family. Men with or without a personal history of prostate cancer who have a family history of prostate breast colon ovarian or pancreatic cancers especially if any of.
Written by Honor Whiteman on March 9 2015. Outcome after radical prostatectomy in young men with or without a family history of prostate cancer. Impact of familial and hereditary prostate cancer on cancer specific survival after radical retropubic prostatectomy.
The risk of prostate cancer also increases as men get older. Men who have a family history of prostate cancer. In general there are three groups of men who should consider genetic counseling and testing for prostate cancer.
Nelson-Aalen estimates with 95 confidence intervals CIs were calculated for cumulative family history-stratified probabilities of any non-low- any of Gleason score 7 prostate. The evidence so far doesnt suggest that routinely screening these men would help prevent deaths from prostate cancer.