Hepatitis B serologic testing involves measurement of several hepatitis B virus HBV-specifi c antigens and antibodies. It rises during the incubation period and may be cleared early in the course of the disease.
 Understanding Hepatitis B Serology Results Youtube
Understanding Hepatitis B Serology Results Youtube
Interpreting hepatitis B serological test results.
Hep b serology. The following discusses the major serologic tests used for hepatitis B diagnosis. Viral Hepatitis Serology Training. HBsAg is the antigen used to make hepatitis B vaccine.
This training is comprised of five animated videos with voiceovers. Hep B serology indicating prior or resolving infection. Hepatitis B surface antigen HBsAg is the hallmark of HBV infection and is the first serological marker to appear in acute hepatitis B and persistence of HBsAg for more than 6 months suggests chronic HBV infection.
Anti-HBs appears 4 wks sp disappearance of HBsAg. An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period - from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. The presence of HBsAg indicates that the person has hepatitis B infection.
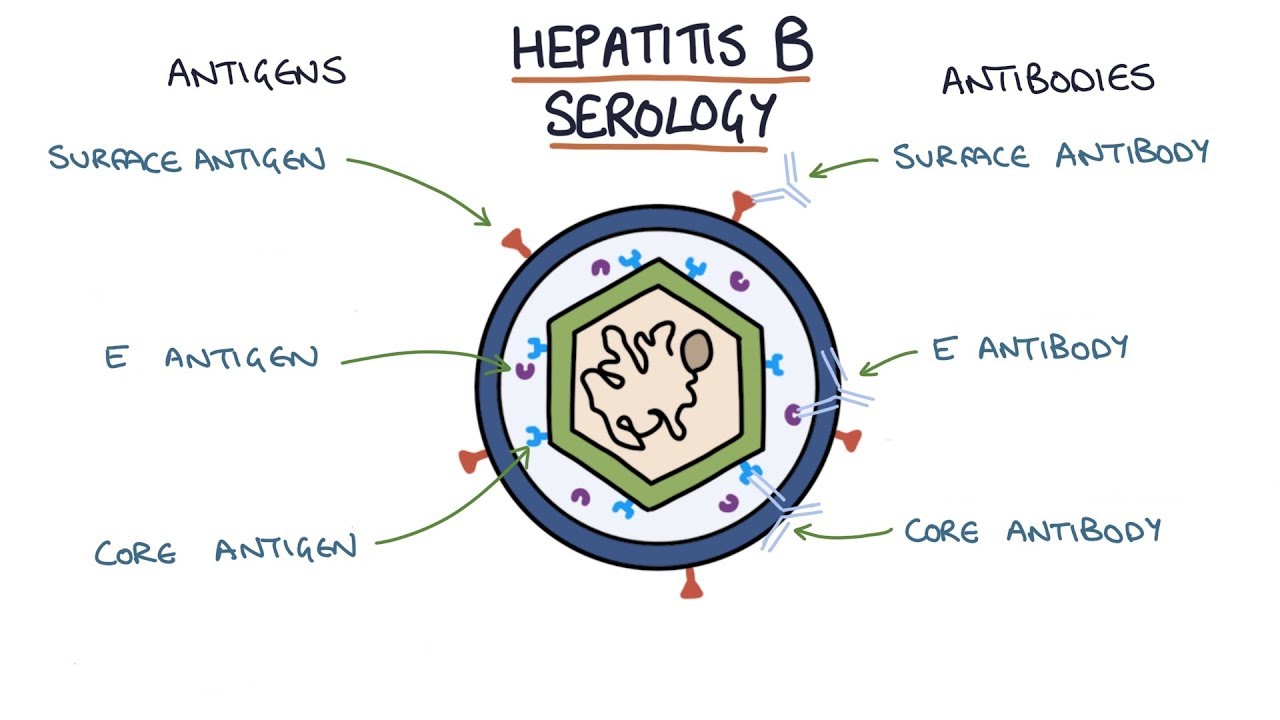
The hepatitis B blood tests are collectively known as the serologic panel. These individuals are infectious to others. Hepatitis B Surface Antigen HBsAg indicates presence of viral envelope and suggests that the person is infectious.
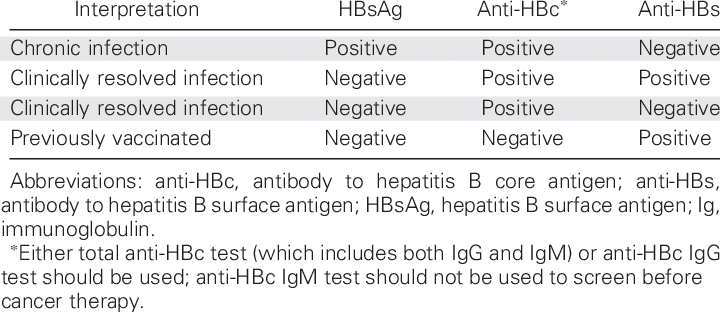
Without postexposure immunoprophylaxis approximately 40 of infants born to HBV-infected mothers in the United States will develop chronic HBV infection approximately one-fourth of whom will eventually die from chronic liver disease. The interpretation of these tests as well as the progression of these markers with acute HBV infection resolved HBV infection chronic HBV infection and response to immunization are summarized in the section Interpretation of HBV Serologic Tests. Since there are a number of markers and at least six interpretations of the various results determining their meaning can be challenging.
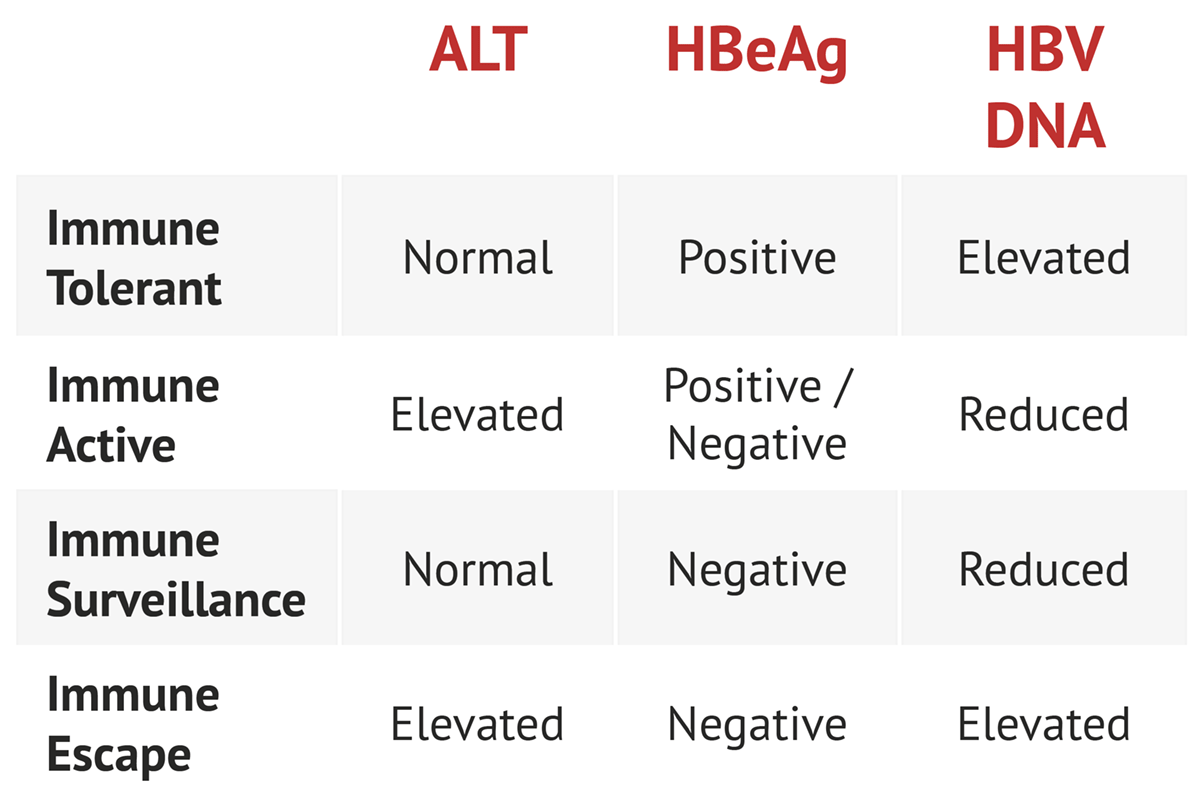
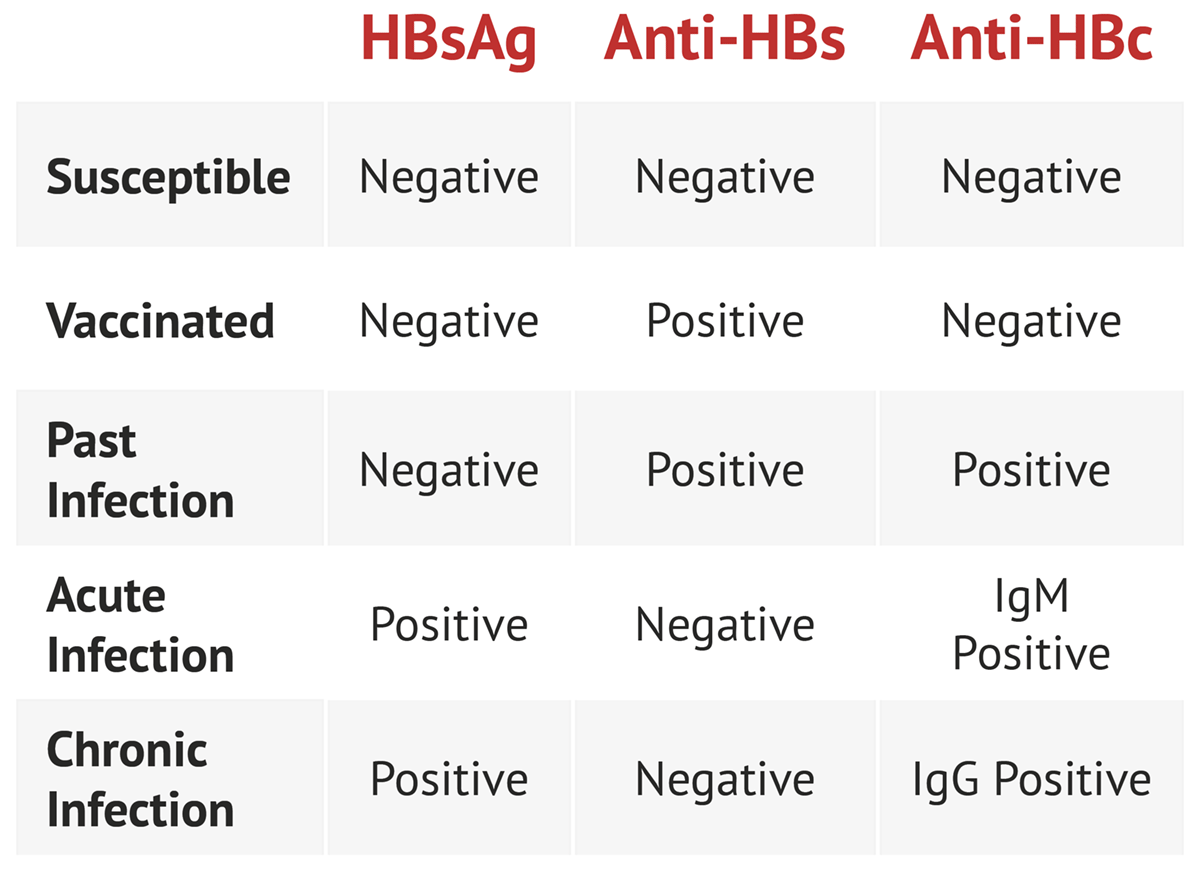
Three different serologic tests are needed hepatitis B surface antigen HBsAg hepatitis B surface antibody anti-HBs and total hepatitis B core antibody anti-HBc to determine whether a patient has acute or chronic HBV infection and is in need of post-test counseling and linkage to care 11. INTRODUCTION The identification of hepatitis B virus HBV infection was revolutionized by the discovery of Australia antigen now called hepatitis B surface antigen HBsAg. Susceptible Immune due to Successful Vaccination Immune due to Resolved infection Acute HBV Prior HBV and isolated HBcAb Test is only needed if patient is HBsAg positive or there is suspicion of occult HBV.
Upon completion of this training participants will be able to understand the different serologic tests for Hepatitis A virus HAV infection Hepatitis B virus HBV infection Hepatitis C virus HCV infection Hepatitis D virus HDV. This set of tests can accurately diagnose current and past hepatitis B infection. Hepatitis B Virus Tests and Interpretation - Hepatitis B.
During the ensuing two decades serologic assays were established for HBsAg and other HBV antigens and antibodies. HBsAg or Surface antigen hepatitis B surface antigen. Clinical Information Hepatitis B e antigen HBeAg is a small polypeptide that exists in a free form in the serum of individuals during the early phase of hepatitis B infection soon after hepatitis B surface antigen HBsAg becomes detectable.
It is undetectable in around 10 of people by the time the test is performed. It can take up to six months however for. Hep B serology signifying recovery immunity.
IgG Anti-HBc persists indefinitely hep B serology present in non-replicative HBV infection. Hepatitis B serological markers Hepatitis B surface antigen HBsAg This is a protein on the surface of the hepatitis B virus HBV. Diagnosis of HBV infection is usually through serological and virological markers.
This is the test that should be ordered for prenatal screening. It can be detected in the serum during acute or chronic HBV infection. Hepatitis B virus HBV infection in a pregnant woman poses a serious risk to her infant at birth.
Indicates either acute hepatitis B infection or more often a carrier of hepatitis B. Post-vaccination serologic testing PVST helps identify infants born to hepatitis B virus HBV-infected women who do not have an adequate immune response to an initial hepatitis B vaccine series and might require additional vaccination. Serum levels of both HBeAg and HBsAg rise rapidly during the period of viral replication.
Different serologic markers or combinations of markers are used to identify different phases of HBV infection and to determine whether a patient has acute or chronic HBV infection is immune to HBV as a result of prior infection or vaccination or is susceptible to infection.
 Hepatitis B Serology Liver Function Tests Medschool
Hepatitis B Serology Liver Function Tests Medschool
Serology Of Hepatitis B Virus Multiple Scenarios And Multiple Exams
 Interpretation Of Hepatitis B Serologic Test Results Download Table
Interpretation Of Hepatitis B Serologic Test Results Download Table
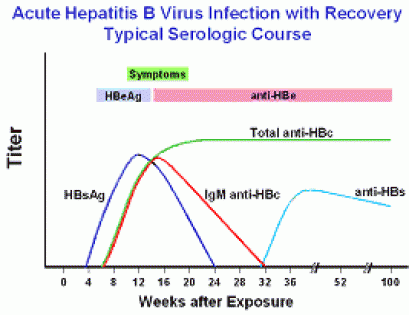 Hepatitis B Foundation Understanding Your Hepatitis B Test Results
Hepatitis B Foundation Understanding Your Hepatitis B Test Results
 Hepatitis B Serology Liver Function Tests Medschool
Hepatitis B Serology Liver Function Tests Medschool
 Hepatitis B Serologies Youtube
Hepatitis B Serologies Youtube
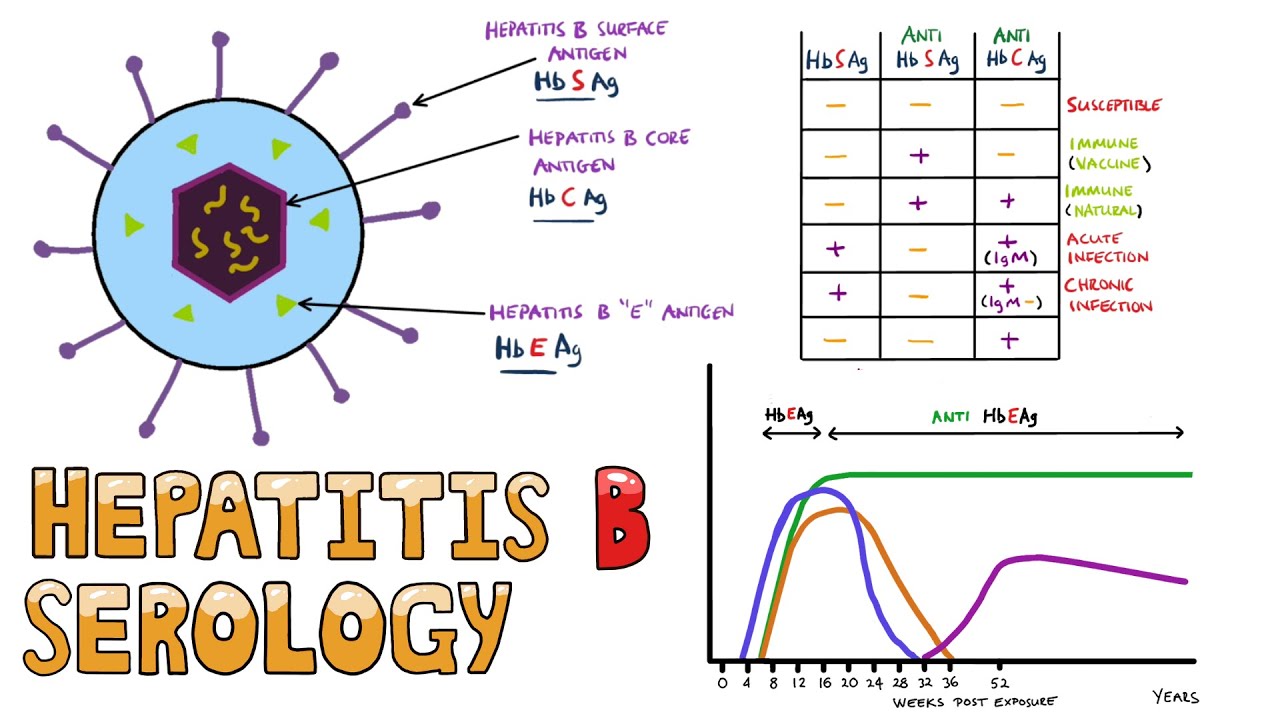 Hepatitis B Serology Made Easy How To Interpret Hepatitis B Serology In Under 5 Minutes Youtube
Hepatitis B Serology Made Easy How To Interpret Hepatitis B Serology In Under 5 Minutes Youtube
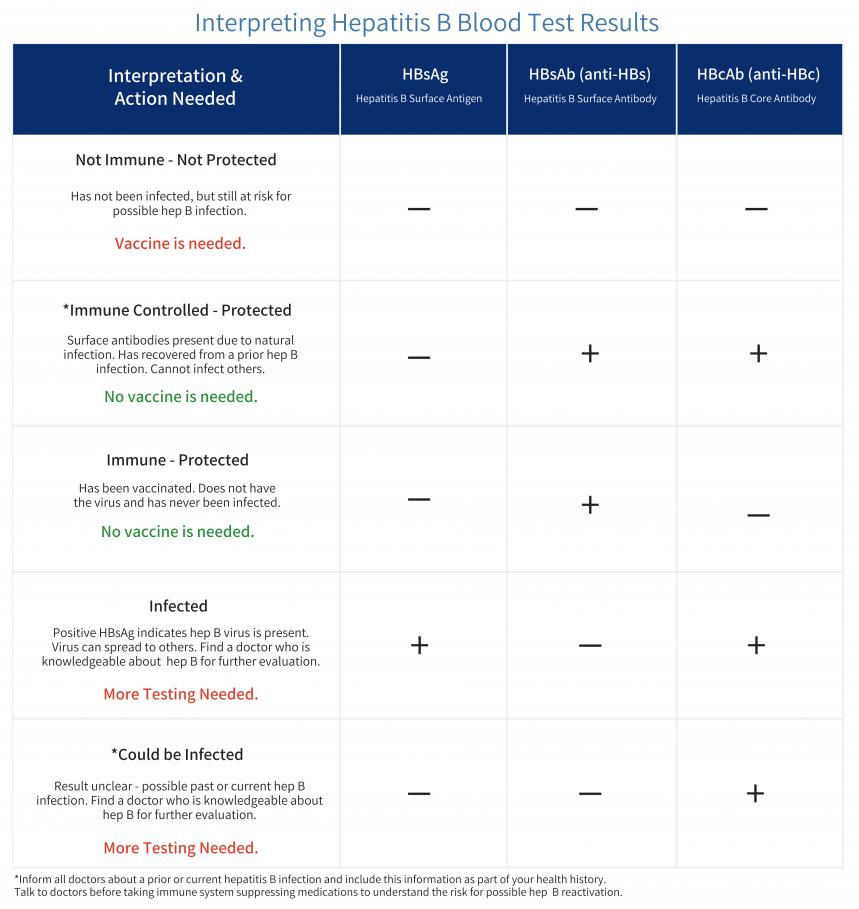 Hepatitis B Foundation Understanding Your Hepatitis B Test Results
Hepatitis B Foundation Understanding Your Hepatitis B Test Results
 Interpretation Of Hepatitis B Serologic Test Results Flashcards Quizlet
Interpretation Of Hepatitis B Serologic Test Results Flashcards Quizlet
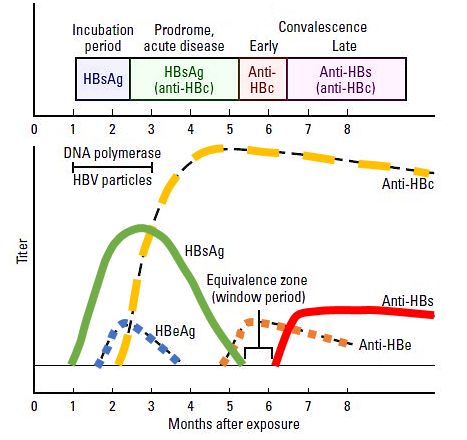 Interpreting Hepatitis B Serology In 5 Easy Steps Epomedicine
Interpreting Hepatitis B Serology In 5 Easy Steps Epomedicine
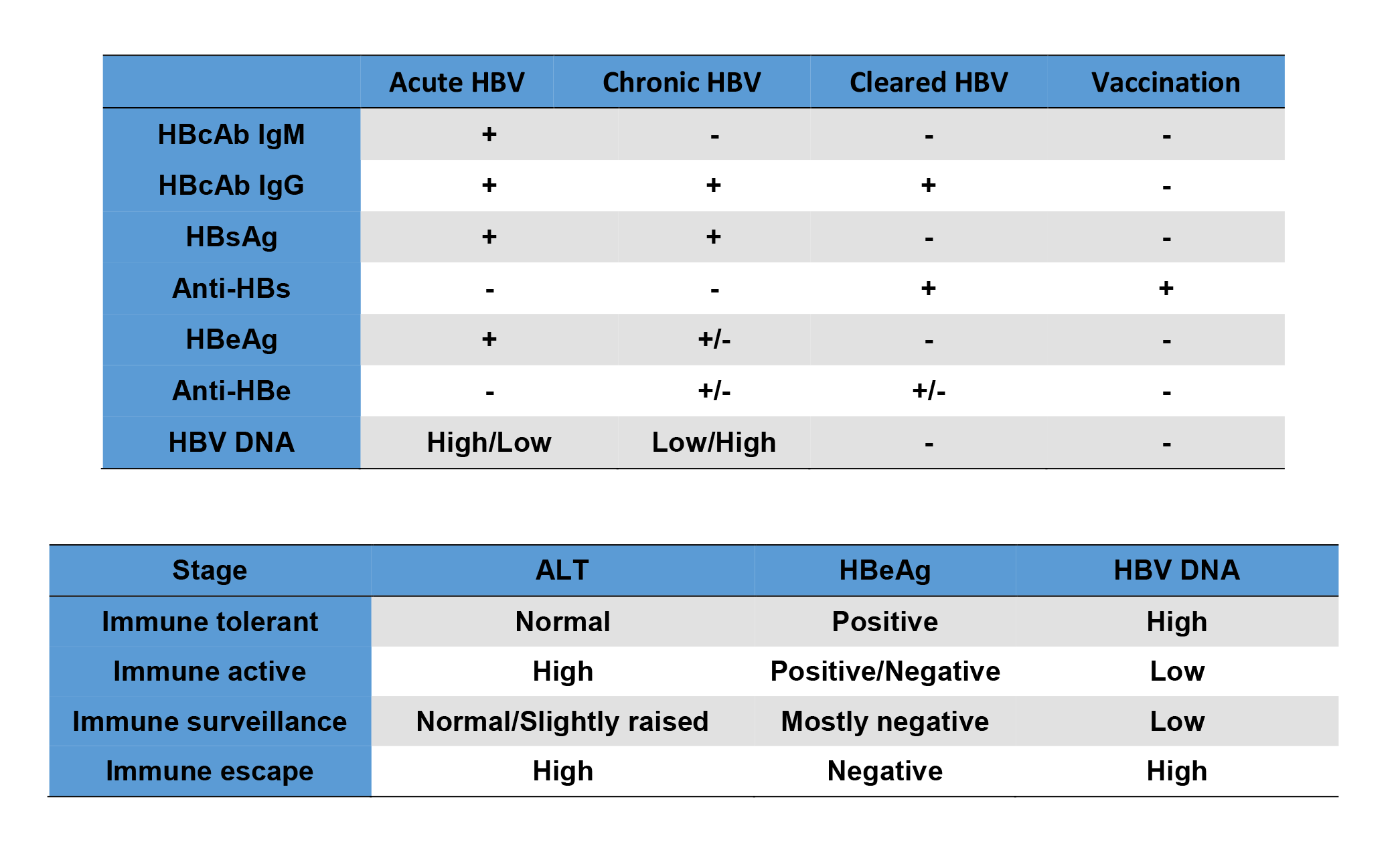 Hep B Serology Viral Markers Oxford Medical Education
Hep B Serology Viral Markers Oxford Medical Education
 Hepatitis B Seromarkers And Serology Interpretation Grepmed
Hepatitis B Seromarkers And Serology Interpretation Grepmed

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.